Variable Usage
Introduction
Variables are the lifeblood of your workflows—they carry data between nodes, making your automations dynamic and context-aware. Every time a node completes execution, its output becomes available as a variable that subsequent nodes can access and use.
Think of variables as containers that hold data as it flows through your workflow. Understanding how to access and manipulate them is key to building powerful automations.
Accessing Variables
Langdock provides two intuitive ways to access variables from previous nodes in your workflow:
Method 1: Double Curly Braces ({{}})
{{}})The most direct way to reference variables is using the double curly brace syntax. Simply type {{ in any field, and you’ll see a dropdown of all available variables from previous nodes.
Basic syntax:
{{node_name.output.field_name}}Real-world examples:
{{form1.output.email}}
{{analyze_feedback.output.sentiment}}
{{api_call.output.data.userId}}
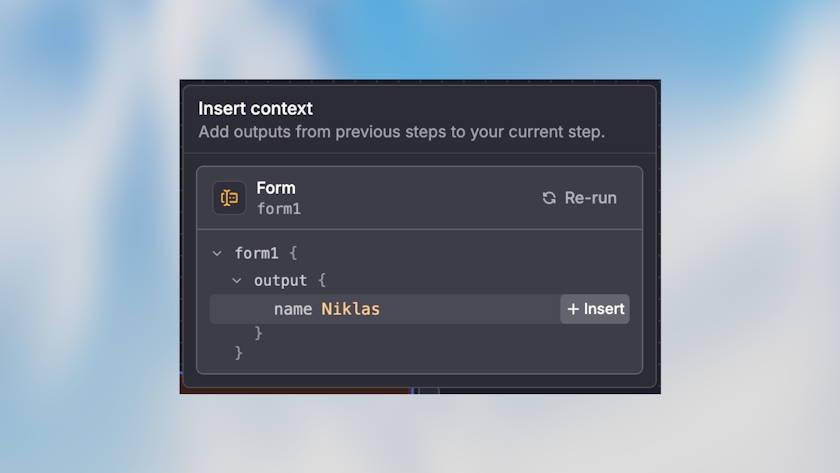
{{trigger.output.customer_name}}Method 2: Output Selector
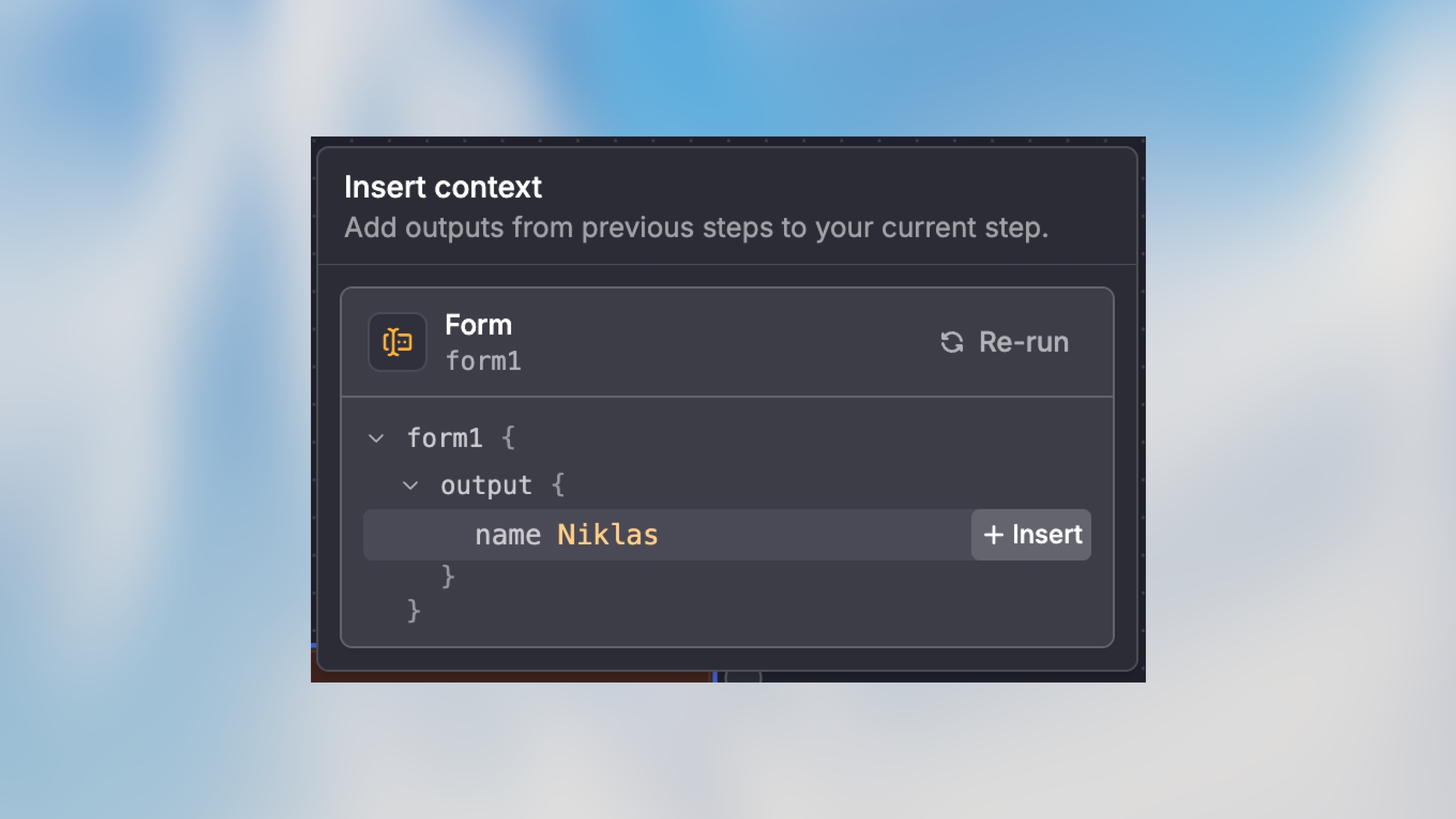
For fields that support it, you can use the visual output selector instead of typing variable paths manually. This is especially helpful when you’re not sure of the exact data structure.
Understanding Variable Structure
Variables follow a consistent structure that makes them predictable and easy to work with:
Breakdown:
node_name: The unique name you gave the node (e.g.,form1,analyze_data,http_request)output: The standard output object every node producesproperty: The specific data field you want to access
Accessing Nested Data
You can access deeply nested properties using dot notation:
Working with Arrays
Access specific elements by index:
Or reference the entire array:
Complex Objects
For structured data from agents or API responses:
What Happens When You Rename Nodes
Node names are tied to variables. When you rename a node, all variables referencing that node are automatically updated throughout your workflow—no manual fixes needed.
Example: If form1 is used like this:
and you rename form1 to PMApplicantForm, all references update automatically:
This automatic update happens in:
Manual mode fields
AI Prompt mode instructions
Code node references
Condition node comparisons
All other node configurations
Best Practice: Name Nodes Meaningfully
Good node names:
ExtractCustomerDataAnalyzeSentimentSendWelcomeEmailCheckInventoryStatus
Avoid generic names:
❌
agent1❌
http_node❌
trigger❌
action
Reusing Variables Across Multiple Nodes
Once a node produces output, that data is available to all subsequent nodes in your workflow.
Basic Variable Reuse
Example usage:
Use Case: Multi-Channel Notifications
Send the same information through different channels:
Advanced Variable Techniques
Combining Multiple Variables
Mix data from different nodes in a single field:
Variables in Code Nodes
Access variables as standard objects in code nodes.
JavaScript:
Python:
Variables in AI Prompt Mode
Reference multiple variables in AI instructions:
Filtering and Transformation
In a Condition node:
In a Code node for filtering:
Troubleshooting Variables
Quick Reference
Variable Syntax Cheat Sheet
Basic field access
{{node.output.field}}
{{trigger.output.email}}
Nested object
{{node.output.object.property}}
{{user.output.profile.age}}
Array element
{{node.output.array[index]}}
{{items.output.list[0]}}
Nested in array
{{node.output.array[0].property}}
{{orders.output.items[0].price}}
Entire array
{{node.output.array}}
{{trigger.output.tags}}
Agent structured output
{{agent.output.structured.field}}
{{analyze.output.structured.summary}}
Multiple in one string
Order {{trigger.output.id}} for {{trigger.output.amount}}
—
Best Practices
Use Descriptive Node Names — e.g.,
{{AnalyzeCustomerFeedback.output.sentiment}}is clearer than{{agent1.output.sentiment}}Test Variables After Each Node — run a test and inspect node output to confirm structure
Provide Fallback Values — e.g.:
Keep Variable Paths Simple — consider a Code node to simplify deeply nested data
Document Complex Variable Usage — add comments in Code nodes or descriptions in nodes for complex logic
Next Steps
Explore these related topics: